Use our plasma stability assay to measure the degradation of your compounds in plasma.
The plasma stability assay is one of Cyprotex's in vitro ADME screening services. Cyprotex delivers consistent, high quality data with cost-efficiency that comes from a highly automated approach.
Introduction
Determination of stability in plasma:
- Determination of the stability of new chemical entities in plasma is important as compounds (with the exception of pro-drugs) which rapidly degrade in plasma generally show poor in vivo efficacy.
- Instability in plasma can result in misleading in vitro data which can be difficult to interpret (e.g., plasma protein binding data). Storing and analyzing clinical samples from in vivo pharmacokinetic studies may also prove challenging.
- Compounds with the following functional groups tend to be more susceptible to hydrolysis in plasma: esters, amides, lactones, lactams, carbamides, sulphonamides, and peptic mimetics1.
- Compounds may exhibit interspecies differences in their stability in plasma.
- Plasma stability is very useful for screening of prodrugs and antedrugs, where rapid conversion in plasma is desirable.
Protocol
Plasma Stability Assay Protocol
Follow on metabolite profiling studies:
Cyprotex's plasma stability assay can be extended to profile the metabolites that are formed. Cyprotex’s biotransformation services are supported by high-resolution, accurate mass spectrometry. These services can provide information on an individual species’ metabolite profile, or a cross-species comparison to identify potential differences in metabolism which could in turn help to interpret pharmacology and toxicity data. Structural elucidation can also be performed on the potential metabolites’ MS/MS fragmentation data. All biotransformation studies are performed by a dedicated team of experts.
Please refer to our Metabolite Profiling and Identification section for further details.
Data
Data from Cyprotex's Plasma Stability Assay
2 compounds were incubated with either human and rat plasma, or dog and mouse plasma over 120 min. These compounds show clear differences in stability following incubations (Figure 1). These data may be useful in interpreting in vivo efficacy, toxicity and pharmacokinetic studies.
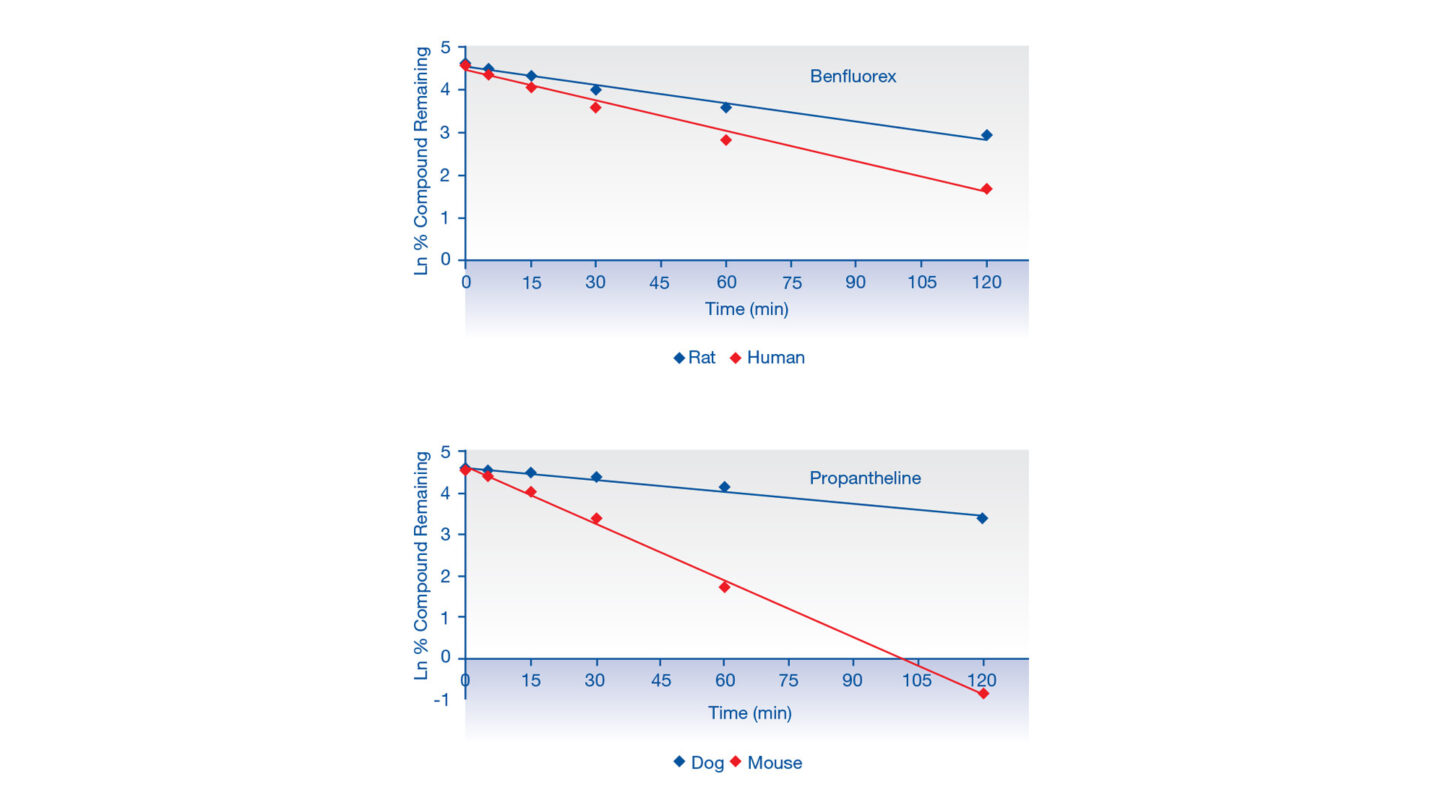
Figure 1
Graphs displaying disappearance of benfluorex in human and rat plasma, and propantheline in mouse and dog plasma over 120 minutes (data is an average from n≥19 across multiple assays and different pooled plasma batches).
Q&A
Please provide an overview of Cyprotex's plasma stability assay.
Cyprotex's plasma stability identifies compounds which are unstable in plasma.
The test compound (final incubation concentration = 1µM) is incubated with plasma (final DMSO concentration = 0.25%) at six different time points (0, 5, 15, 30, 60 and 120 min). The reaction is terminated by acetonitrile containing internal standard. Following centrifugation, the disappearance of test compound is monitored by LC-MS/MS. The half-life and the percentage of test compound remaining at the individual time points relative to the 0 minute sample are then reported. A control compound known to be metabolized by plasma esterases is also incubated alongside each batch of test compounds.
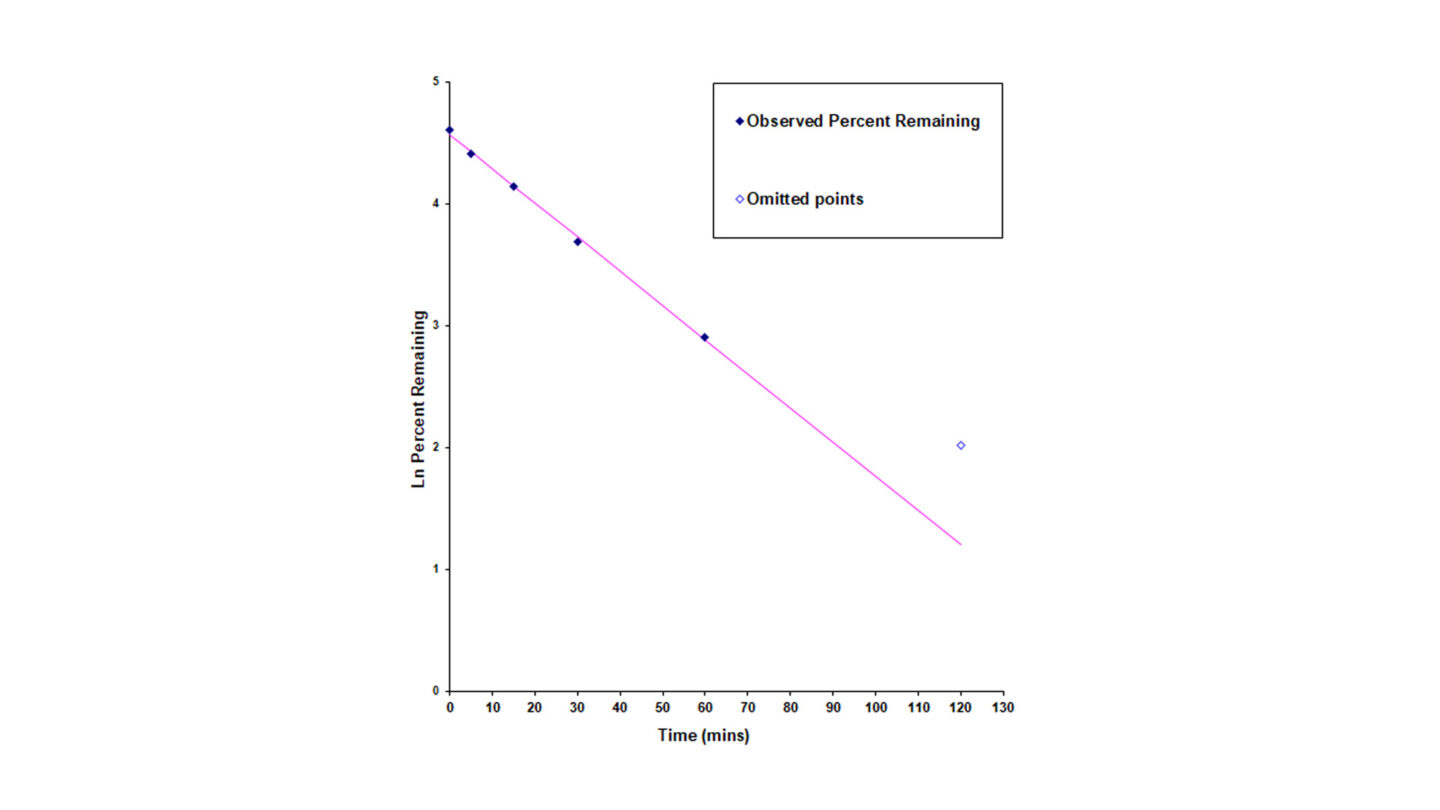
Figure 2
Stability of benfluorex in human plasma over 120 minutes. The half-life is calculated using the following equations below:
Why is determining plasma stability important?
Typically, unless the compound is a pro-drug, instability in plasma can be detrimental as the concentration of compound in vivo will be reduced which, in turn, influences efficacy. Difficulty may also be experienced in measuring and interpreting the data from in vitro plasma protein binding studies. Storing and analyzing clinical samples from in vivo pharmacokinetic studies may also be challenging.
How do you ensure equivalent recovery from the plasma for all the samples?
When validating the assay, 4 compounds were tested to confirm recovery of compound when spiked into 100% human plasma, and were immediately quenched with varying solvent ratios. Testing was completed at 0, 1 and 2 hours of sample being quenched before centrifugation. Data showed consistent recovery in all conditions when compared to a 1 µM post-extraction spike. This provides confidence in extraction efficiency regardless of time prior to centrifugation.
How do you know if the compound is degraded by enzymatic processes?
In order to confirm that degradation is caused by enzymatic processes, it is recommended that the compound is also screened through relevant buffer matrix.
What classes of compounds are metabolized by plasma?
Typically, plasma stability is performed as a secondary screen for particular classes of compounds which feature functional groups more susceptible to hydrolysis in plasma. These include esters, amides, lactones, lactams, carbamides, sulphonamides, and peptic mimetics1.
How are pro-drugs studied in this assay?
If the assay is being used to screen for pro-drug stability and active compound can also be supplied then we can monitor disappearance of pro-drug and appearance of the active compound simultaneously.
Reactions are terminated using acetonitrile. This is to try and minimize any transesterifcation of the pro-drug which may occur in the presence of methanol.
Can you investigate stability in matrices other than plasma?
We can investigate stability in other matrices for example; blood, tissue homogenates and buffer.
References
1) Di L et al. (2005) International Journal of Pharmaceutics 297; 110-119